Significance
HIV evolution inside contaminated people creates massive obstacles to profitable vaccination and remedy. Right here, we used a mannequin that matches viral masses and mutation charges to characterize the driving forces behind HIV evolution early throughout an infection. Surprisingly, the most effective mannequin of the info didn’t require express strain from the host immune system. As a substitute, the mannequin predicts most new viral variants are intrinsically worse at infecting new cells relative to their dad and mom. Thus, most variants don’t persist and solely by occasional probability does a brand new match variant come to dominate. These findings additionally spotlight the tight connection between viral inhabitants dynamics and evolution, warranting extra modeling to disentangle these processes sooner or later.
Summary
Trendy HIV analysis relies upon crucially on each viral sequencing and inhabitants measurements. To straight hyperlink mechanistic organic processes and evolutionary dynamics throughout HIV an infection, we developed a number of within-host phylodynamic fashions of HIV main an infection for comparative validation towards viral load and evolutionary dynamics information. The optimum mannequin of main an infection required no constructive choice, suggesting that the host adaptive immune system reduces viral load however surprisingly doesn’t drive noticed viral evolution. Reasonably, the health (infectivity) of mutant variants is drawn from an exponential distribution by which most variants are barely much less infectious than their dad and mom (almost impartial evolution). This distribution was not largely completely different from both in vivo health distributions recorded past main an infection or in vitro distributions which are noticed with out adaptive immunity, suggesting the intrinsic viral health distribution might drive evolution. Simulated phylogenetic timber additionally agree with impartial information and illuminate how phylogenetic inference should take into account viral and immune-cell inhabitants dynamics to achieve correct mechanistic insights.
Longitudinal sequencing of HIV over time in an contaminated particular person offers invaluable insights into the pathogenesis of illness. Phylogenetic instruments (1) assist illuminate evolutionary relationships between viral sequences and phylodynamics leverages such relationships to additional infer underlying processes governing evolution (2, 3). Nonetheless, phylodynamic instruments typically don’t embody the small print of within-host HIV an infection, which embrace large exponential expansions and contractions of viral populations, mounting immune responses, goal cell limitation, and existence of short- and long-lived cell populations. Mechanistic mathematical fashions of HIV explicitly embrace these predator/prey interactions and are amenable to generalized nonlinear processes together with therapeutic interventions (4). Subsequently, unifying intrahost mechanistic modeling with phylodynamics is a probably highly effective strategy to disclose the mechanisms underlying intrahost viral evolution that hinder HIV prevention and/or remedy.
There’s an in depth historical past of modeling unified phylodynamics for viruses inside and between hosts (5⇓–7). Inside-host HIV fashions have modeled nucleotide sequences and assumed multistrain phenotypes with health distributions (6⇓⇓⇓⇓⇓–12). Explicit elements of HIV biology together with recombination (13, 14), drug resistance (15), antibody evolution (16, 17), adaptive immunity (18, 19), and latency (20) have been thought-about. A number of common ahead simulation packages can be found (21⇓–23). Our work grows from these and different fashions. Right here we sought to establish mechanistic drivers of HIV evolution by figuring out and validating a within-host phylodynamic (WiPhy) mannequin towards a spread of experimentally collected HIV information. By constructing in capabilities of the mannequin to simulate information that may be exported and analyzed by current phylogenetic inference software program, we corroborate the physique of labor exhibiting that with out correct fashions for inhabitants dynamics, phylogenetic timber can inaccurately infer phylodynamics.
The WiPhy mannequin is then used to handle the continuing query of how and the way a lot the host immune system influences within-host HIV evolution. Beforehand, immune management over viremia has been elegantly demonstrated in nonhuman methods by fast will increase in viral masses following CD8+ T cell depletion (24⇓⇓–27). But, the extent of immune strain on viral evolution is more durable to watch straight. Selective strain and coevolution of CD8+ T cells has been inferred from matching HIV mutations to circulating CD8 epitopes (28⇓⇓–31), computing the ratio of synonymous to nonsynonymous mutations in HIV sequences (32), linking the prevalence of escape mutations to host-genetic predispositions reminiscent of HLA sort (33) (human leukocyte antigen, genes that regulate immune operate), and modeling (19, 34). Nonetheless, express escape from mobile immunity will not be at all times apparent. Utilizing information from 125 adults within the SPARTAC trial (33) Roberts et al. discovered most people had no detectable escape mutants inside 2 y of an infection. Early mutations (<6 mo after seroconversion) have been principally transmitted, fairly than arising from fast de novo escape within the new host. Even in an HLA-matched host who mounted a measurable and HIV-specific CD8 response, the common time earlier than the focused epitope developed an escape mutation was longer than 2 y. Lee et al. additionally discovered 4 clade-C-infected people had little indication of cytotoxic T cell-driven immune alternatives within the first yr (35). Neutralizing and broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs) are also thought to work together and coevolve with founder viruses over the course of HIV an infection (36, 37). But, bNAbs can come up shortly with out many mutations (38) and in infants (39). Lately, Strauli et al. analyzed information of unprecedented element on each HIV and antibody repertoire sequences, finally discovering that HIV/Ab coevolution is at minimal exhausting to detect, if not uncommon totally (40).
In that context, we discover that probably the most parsimonious mannequin of HIV main an infection requires adaptive immunity to manage viral load however doesn’t require the adaptive immune system to straight choose for sure variants. Sequence evolution can as an alternative be managed by a distribution of intrinsic viral health the place most variants are much less infectious than their dad and mom. We present the model-predicted viral health distributions agree with that of HIV deep mutational scanning (DMS) which quantifies health in vitro, essentially within the absence of immune strain. By constructing a mannequin that features host and virus inhabitants dynamics in addition to mutation, our work highlights essential questions on HIV evolution related to vaccines and therapeutics.
Outcomes
Viral Dynamics and Phylogenetics throughout Main HIV An infection.
We sought to establish an optimum mannequin for HIV main an infection phylodynamics. Subsequently, we first collected 4 datasets related to early HIV an infection: 1) nonlinear viral dynamics throughout early HIV an infection, 2) longitudinal divergence and variety, 3) put up antiretroviral remedy HIV reservoir dimension and composition when it comes to faulty and intact sequences, and 4) tree-balance measures (see SI Appendix, Table S1 for particulars and references).
Subsequent, to quantitatively rating fashions towards these information, we developed 10 phylodynamic metrics: viral kinetic measures (peak, set level, and set level variability), evolutionary measures (HIV envelope, or env, divergence and variety on days 20 and 40 after an infection), and ratio of intact to all proviral sequences within the HIV reservoir (see Supplies and Strategies and all definitions and values in SI Appendix, Table S2). As a result of no particular person dataset had sufficiently granular information for every type, we opted to suit to inhabitants information throughout varieties. This determination implies the mannequin describes a typical HIV an infection. Parameter values are subsequently much less particular and have larger variance than people who is likely to be estimated by becoming to people. Alternatively, tighter particular person estimates could possibly be extra biased by options of the precise cohort and probably much less reflective of your complete vary of HIV infections.
WiPhy Mannequin for HIV Main An infection.
We started with a common stochastic WiPhy mannequin that extends the canonical viral dynamics mannequin (41) by including latency and adaptive immunity and contains viral variants that mutate (Fig. 1A). Every variant corresponds to a singular genotype (signified by an integer g). Evolution is then tracked by recording the whole family tree (or transmission report) of those genotypes (). We report attributes for every genotype that enable reconstruction of phylogenetic timber and calculation of evolutionary abstract statistics: father or mother genotype, infectivity, Hamming distance (HD) to the founder sequence, variety of every nucleic acids (ACTG), and age.
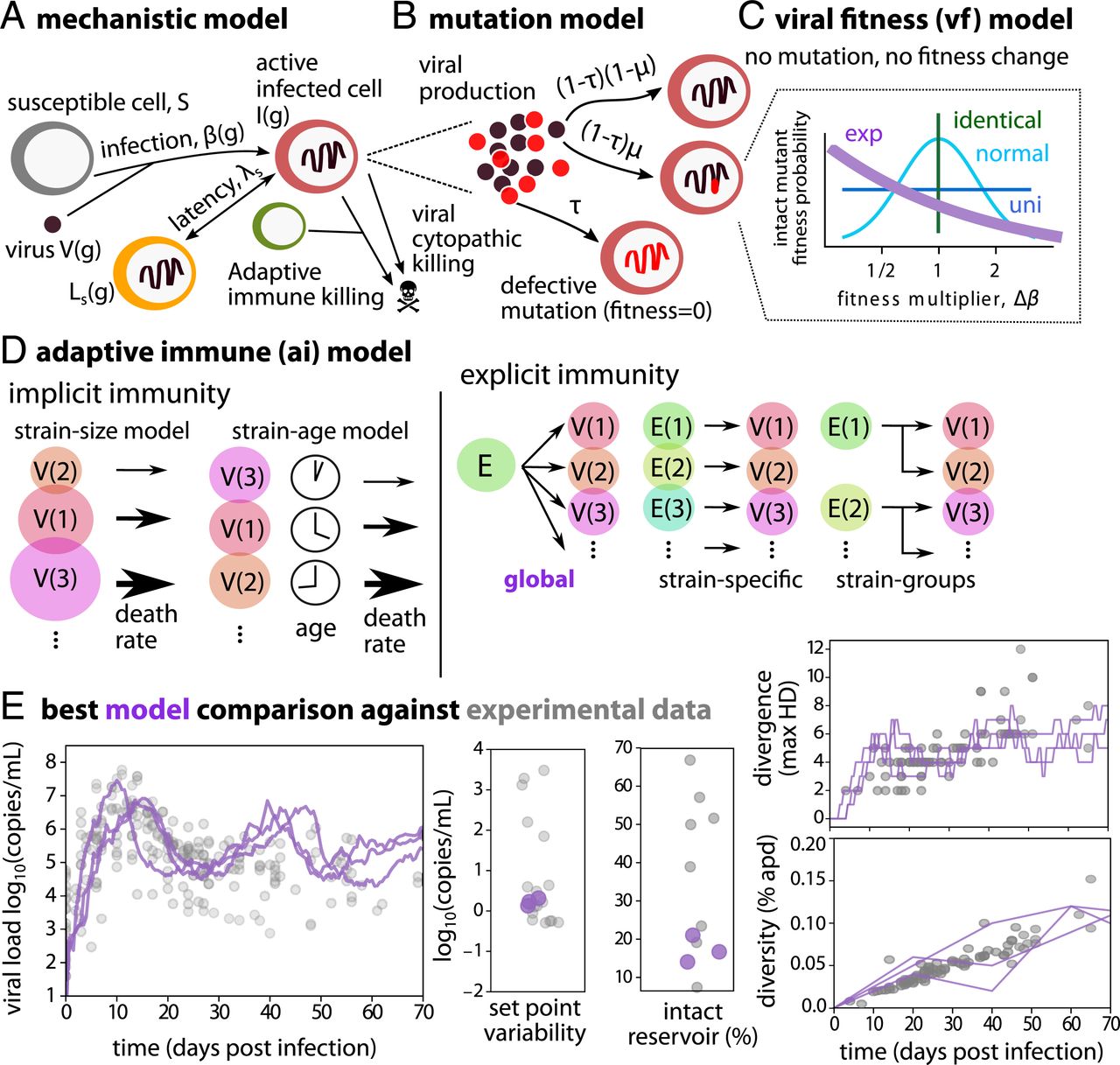
Mechanistic WiPhy fashions and the optimum match to experimental information. (A) Mechanistic mannequin schematic. Inclined cells are contaminated by viral variant with a genotype , producing new contaminated cells (latent and lively), producing extra virus, and engendering immune responses. (B) Mutation mannequin governs new variants which are faulty (likelihood τ) or intact. (C) If intact, level mutations (likelihood μ) can happen that change variant health (infectivity) based mostly the viral health (vf) mannequin—exponential mannequin was optimum. (D) Adaptive immune (ai) fashions have been additionally different—world was optimum. (E) Three stochastic replicate simulations of the most effective mannequin (exponential-global, purple) towards the 5 forms of experimental information (grey, see SI Appendix, Table S1 for particulars on information and cohorts).
Upon cell an infection, the virus can mutate (likelihood μ). Most mutants are terminally faulty however some variants stay intact (with likelihood τ) (Fig. 1B). New intact variants are given a brand new genotype () and a brand new infectivity () drawn from a distribution (Fig. 1C). All through, we characterize variant health utilizing infectivity. Adjustments can’t be ascribed to mutation of a sure genomic locus, that’s, there isn’t a genotype/phenotype hyperlink within the mannequin. Nonetheless, nucleotide sequences could be reconstructed from the family tree to allow alignment and phylogenetic tree reconstruction (see Fig. 4). Collectively, this formulation allowed us to simulate massive inhabitants sizes (109 viruses in 10 mL of blood) with good temporal decision (Δt = 0.01 d), compute all phylodynamic metrics, and join simulated information to phylogenetic timber. All code is freely obtainable at https://github.com/FredHutch/WiPhy_HIV.
Mathematical Mannequin Choice towards Phylodynamic Metrics from Main HIV An infection.
To find out the mechanisms required to precisely match experimental information, we tried to suit 24 distinct mechanistic fashions. For viral health (vf, Fig. 1C), we examined 4 fashions: all new variants have the identical health (vf-identical), all new variants have a randomly assigned health (vf-random), and two fashions the place variant health was inherited, both based mostly upon an exponentially (vf-exp) or usually distributed (vf-normal) change from its father or mother sequence. For adaptive immunity (ai, Fig. 1D), we examined six fashions: one with no adaptive immunity; two the place immune strain was implicit, both based mostly upon the dimensions of a sure sequence inhabitants (ai-size) or the size of time {that a} sure sequence existed (ai-age); and three the place immune strain was express—that means a compartment of the mannequin was added—both based mostly upon a situation the place adaptive immune cells can kill any HIV sequence (ai-global) or adaptive immune cells have a particular cognate genotype which they will solely kill (ai-specific) or adaptive immune cells can kill a spread of genotypes (ai-groups). Within the third class, a typical dynamical mannequin for adaptive immune cells was included that enables adaptive cells to develop and shrink in quantity based mostly on the commensal contaminated cell depend. Immune cell era will not be limitless, and creation saturates if a sure worth is reached (see Eq. 3).
For every mannequin, 100 parameter units per mannequin parameter have been examined and 20 stochastic replicates have been tried, stopping if 10 have been reached. This amounted to 104,497 simulations (or roughly 72 simulation days at 1 min per run). We decided profitable fashions as these with a balanced match to all phylodynamic metrics: an approximate Bayesian computation (ABC) strategy (see Supplies and Strategies) (42). SI Appendix, Fig. S1 reveals the entire scores of the most effective single stochastic runs, in addition to the most effective parameter units that match nicely throughout stochastic runs.
The perfect single run and the most effective common rating throughout stochastic replicates was achieved by the “exponential-global” mannequin that’s ruled by an exponential intrinsic health distribution for viral offspring and a single adaptive immune compartment that kills globally, i.e., removes all viral strains equally. This mannequin had a normalized residual sum of squares (RSS) two or extra factors decrease than all different fashions. Whatever the adaptive immune mannequin, many of the high fashions had the exponential health distribution. The conventional viral health mannequin with no adaptive immunity in any respect got here in third for the stochastic runs, suggesting it will possibly do nicely on a given stochastic run, however didn’t fall into the highest 5 fashions when averaged throughout stochastic runs. Particular person mannequin traces are in comparison with information metrics in SI Appendix, Fig. S2, which reveals that visually a number of of the highest 5 fashions seem to suit fairly nicely. To go additional, in SI Appendix, Fig. S3 we illustrate that viral load set level and variety later than 40 d seem to place the strongest filter on fashions, with exponential-global outperforming all different fashions in these classes.
We have been significantly serious about why a mannequin by which particular person adaptive immune compartments kill particular viral strains—probably the most literal model of host-on-pathogen selective power—was unsuccessful. SI Appendix, Fig. S4 reveals that the exponential-strain mannequin was not able to reaching a low sufficient viral load set level, suggesting there’s a stability between sustaining range and set-point degree that’s exhausting to realize by uneven immune strain to sure strains.
In abstract, though it appeared that single stochastic runs of a number of fashions might carry out fairly nicely, averaged throughout stochastic replicates the exponential health distribution was optimum for all adaptive immune fashions. Moreover, by this quantitative scoring system, world immune strain was optimum, with complete RSS better than 4 factors decrease than the closest competing fashions.
Implications of an Optimum Mannequin with Nonspecific Immunity and Inherited Exponential Viral Health.
Three stochastic replicate simulations of the most effective mannequin and finest parameter set are in comparison with information in Fig. 1E. Particular person traces are imperfect however all metrics (viral load peak, nadir and set level, set level variability, sequence divergence, sequence range, and intact and faulty latent reservoir dimension) have been captured inside our tolerance.
A number of mechanistic outcomes are implied by the optimum WiPhy mannequin. Requiring inherited health signifies that lineages persist by probability past single-cell lifetimes. Quantitatively, our mannequin predicts that advantageous mutation happens in 11% of intact mutations, and intact are solely ∼5% of all mutations. The typical intact mutant has roughly half (0.47) the infectivity of its father or mother [e.g., a nearly neutral process (43)] such that almost all lineages die out and go away room for brand spanking new variants. Importantly, strain-specific adaptive immune strain was not essential to seize the most important options of within-host HIV phylodynamics in early an infection. Neither a mannequin the place viral strains implicitly misplaced health over time nor fashions with express strain-specific immunity matched the info in addition to one with a broad immune response that killed all variants. Reasonably than immune-mediated choice sweeps, our mannequin favors fixed mutations and fluctuations in intrinsic viral health as the first mechanistic driver of noticed HIV evolution throughout main an infection.
Self-Consistency of Mannequin Choice.
To verify that the mannequin choice course of was sturdy, we carried out a self-consistency train. Information simulated by a given mannequin and parameter set have been used because the experimental information and the mannequin choice course of was repeated. For many fashions (and most parameter units), it was potential to accurately choose the mannequin that generated the info (SI Appendix, Fig. S5). We additionally assessed the efficient dimensionality of mannequin output, discovering {that a} substantial quantity (∼80%) of mannequin variation is encompassed by two principal parts (pc1 and pc2, SI Appendix, Fig. S6) and that inside these parts many fashions overlap. The comparatively low efficient dimensionality helps to clarify why one (or a number of) metrics can present distinctive signatures that differentiate between fashions. The overlap reveals what number of fashions can match fairly nicely (although not optimally). Collectively, these checks emphasize the individuality of mannequin output and strengthen confidence within the choice course of.
Mannequin-Estimated Health Distribution Resembles In Vivo Health Distributions Not Restricted to Main An infection.
Subsequent, our mannequin’s prediction that HIV evolution could be defined within the absence of particular adaptive immunity was examined towards a special dataset: in vivo entropy distributions from sequences not restricted to main an infection. A reranked Shannon’s entropy was employed as a quantitative estimate of the relative impact of lowering health after a degree mutation. After placing experimental and model-predicted distributions on the identical scale (as a result of there isn’t a absolute scale for entropy), there the form of the 2 distributions was not considerably completely different (Fig. 2). Disagreement arose solely in ranges of bigger health prices ( < 0.25). Thankfully, this vary is much less biologically related as a result of variants experiencing massive health prices, no matter exact worth, are subdominant and don’t considerably affect information or simulations. Importantly, though our authentic mannequin validation used main an infection information, the model-derived intrinsic viral health distribution additionally approximated health distributions from power an infection information, suggesting that our conclusions about viral evolution would possibly pertain in different phases of an infection.
Mannequin-predicted health distribution resembles in vivo information not restricted to main an infection in addition to in vitro information with out the affect of adaptive immune strain. The exponential distribution predicted by the mannequin was in comparison with obtainable in vivo sequence entropy and in vitro DMS information that quantified the relative health of all amino acid modifications inside env. Ranked health has related fractions advantageous. Distributions weren’t considerably completely different by paired Kolmogorov–Smirnov checks. (Inset) Cumulative distribution features (cdf).
Mannequin-Estimated Health Distribution Resembles In Vitro Health Distributions.
It’s troublesome to know whether or not the viral health distribution could possibly be conflating viral health and adaptive immune choice. Thus, we subsequent in contrast the model-estimated distribution with one other dataset: DMS of HIV env (44, 45). DMS quantifies the relative health of in vitro-generated variants (perturbing almost all amino acids in env). The distribution resembles the model-estimated health distribution and each distributions comprise an analogous proportion (∼10 to fifteen%) of advantageous mutations (Fig. 2) and distributions weren’t considerably completely different (Fig. 2, Inset). The most important health enhancements in vivo have been typically lower than these in vitro, such that we can’t rule out that intrinsically match variants are lowered by immunity. This doesn’t battle with the mannequin by which adaptive immunity reduces all variants. It is also unclear whether or not the identical variants which are extraordinarily slot in vitro would essentially succeed as nicely in vivo for causes apart from immunity. These information reinforce that it’s adequate to explain HIV phylodynamics throughout main an infection with out together with constructive choice by adaptive immunity.
World sensitivity evaluation reveals adaptive immune response has a robust influence on viral load however restricted influence on viral evolution.
To check the influence of the adaptive immune compartment additional, we carried out a worldwide sensitivity evaluation by concurrently various all parameters of the most effective mannequin and calculating the Spearman correlation coefficient between all parameters and all abstract statistics (SI Appendix, Fig. S7A). Importantly, of all parameters, the adaptive immune killing charge κ had the strongest influence on the drop to nadir and setpoint, illustrating the significance of the immune system on controlling viral dynamics, particularly after a excessive peak viral load. Parameters regulating the maximal depth of the immune response (saturation phrases for each killing and recruitment ) had minimal influence on all metrics in contrast with different parameters. There was minimal correlation amongst adaptive immune parameters and phylodynamic measures (range and divergence at days 20 and 40) and common infectivity was the strongest determinant of phylodynamic metrics—becoming scores for phylodynamic measures present this sample much more strongly (SI Appendix, Fig. S7B). Collectively, these observations recommend that adaptive immunity’s impact on evolution is oblique by viral load modulation. SI Appendix, Fig. S7C reveals predicted connections between inhabitants dynamic and phylodynamic measures that can’t be calculated from these information (as a result of metrics are from completely different people). Basically, there have been robust correlations inside inhabitants dynamic measures and phylodynamic measures however little correlation between these two broad classes. There was a notable lack of correlation between peak viral load and phylodynamics at or after day 20. Whereas comparatively weak, nadir and set-point viral load have been correlated with phylodynamics, emphasizing the secondary influence of adaptive immune strain on evolution by lowered viral load.
Single-Variant Viral Dynamics throughout Early HIV-1 An infection.
The perfect-fit mannequin was employed to research particular person variant viral dynamics. First, we tracked variants’ viral masses by genotype (Fig. 3A). In the course of the first 3 wk of an infection there have been just one,000 variants, whereas by day 60 >300,000 productively infectious viral genotypes had been produced, that means many extra faulty variants had been created. At roughly day 40, inhabitants sweeps appeared (a brand new variant reaching high abundance) and abundances of concurrent sequences turned more and more even. As defined above, the inhabitants sweeps should not attributable to strain-specific concentrating on by the immune system however by continuous mutations following the exponential intrinsic viral health distribution. Subsequent, realigning variants to their time of emergence (setting when the variant entered the highest 10; Fig. 3B) recognized two dominant kinetic profiles. The primary have been variants from earlier than and through peak viremia, which have a big spike of >105 viral copies (crimson/yellow); the second have been principally generated after day 60 (when world adaptive immunity was considerable), which peak at ∼104 viral copies and slowly decay (blue).
Visualizing evolutionary dynamics within the optimum mannequin. Instance simulation of the most effective mannequin (variants ever in high 10 and complete viral masses). (A) Coloring by genotype quantity illustrates inhabitants sweeps and >106 intact variants; many extra faulty variants have been created. (B) Variant trajectories shifted to the time they entered the highest 10 by abundance; variants rising later in an infection have completely different kinetic profiles than these from early an infection (evaluate crimson and blue). (C) Coloring by HD to founder sequence illustrates most early (crimson) variants have roughly one level mutation from the founder sequence, whereas later sequential evolution has occurred, with variants rising with greater than two mutations from the founder sequence. (D) Proportional abundance coloured by HD illustrates the stark shift from founder predominance to extra evenness after viral load nadir. (E) The whole transmission report, or family tree illustrates the “true tree”—the parental genotype of every variant created on every day. Sure lineages persist for greater than 100 days, that means that offspring are generated from a parental sequence that was created months prior. (F) The tMRCA of fifty randomly sampled sequences on a given day is bimodal: Variants are created by each extra ancestral and more moderen dad and mom.
Coloring the variants as an alternative by their HD from the founder virus (Fig. 3C) revealed a starlike phylogeny that dominates for about the primary 40 d—that means that whereas many distinct variants have emerged, they’re all just one or two mutations away from the founder virus, and that the founder virus stays the mutual widespread ancestor. A shift from a starlike phylogeny arrives as sequential mutations happen; variants emerge with three or 4 base pair mutations from the founder round day 50. The predominance of the founder virus for the primary 40 d can be evident by inspecting proportional abundance (calculated because the ratio of every variant viral load to the entire; Fig. 3D). When the founder loses dominance the opposite variants are equally aggressive, and thus a extra even stability of a number of variants turns into obvious. The timing of those outcomes agrees with impartial information exhibiting shifts from demographic to selective results round day 50 (46).
Extremely Granular Simulated Phylogenetic Bushes.
The flexibility to entry the whole transmission report from these simulations permits examination of evolutionary relationships with excessive granularity. Fig. 3E demonstrates how lengthy sure lineages persist by plotting the parental genotype of every variant sampled on a given day. For instance, the founder variant (g = 0) and different variants (e.g., g = 100) are prolific, producing new direct descendant variants that may be discovered for months. This timescale far outlasts the lifespan of any single contaminated cell (∼1 d) and this mechanistic mannequin has no adaptive immune choice. Subsequently, lineage persistence is a probabilistic stability between viral manufacturing and deleterious mutation of offspring. Moreover, some variants do persist at subdominant ranges; gaps on the x axis point out occasions between which a parental variant was not dominant to the purpose the place its progeny have been assured to be sampled.
Calculating the occasions to most typical ancestor (tMRCA) all through an infection for all pairs of subsampled sequences (n = 50 at every time level) revealed a bimodal distribution with cocirculating lineages (Fig. 3F). For instance, most sampled sequences on day 200 (inexperienced) coalesced to widespread ancestors ∼10 to 40 d previous to the sampling date. This represents a time-localized quasi-species that’s generated actively by a dominant circulating variant. Nonetheless, a minority coalesced to extra ancestral sequence, representing the persevering with influence of prolific early variants. Notice bimodality will not be pushed by latency and reactivation; related outcomes have been discovered utilizing a mannequin with out latent compartments.
Mannequin Validation with Estimated Phylogenetic Bushes within the First 12 months of An infection.
Phylogenetic timber are generally used as an example patterns in HIV evolution. We subsequently examined whether or not the chosen exponential-global mannequin might present cheap settlement with one other impartial dataset, a phylogenetic tree from a extremely sampled particular person within the first yr of an infection (47) (p1362, Fig. 4A). To accommodate all sources of variability in evaluating to the experimental information, three simulations with the most effective mannequin, three sequence samplings from every simulation, and three tree estimation replicates [in BEAST (48)] have been carried out on every pattern set. This course of admits 27 phylogenetic timber (1.1.1 → 3.3.3); two examples are illustrated in Fig. 4B, which appeared visually just like the person p1362.
Comparative evaluation of experimental and mannequin tree estimation. (A) Experimental tree (C1V2 env, p1362). All sampling schemes are based mostly on this particular person. (B) Working the most effective mannequin thrice (i), sampling sequences with similar timing and pattern dimension thrice (j), and with three tree estimate replicates (okay) resulted in 27 timber enumerated i.j.okay. Two instance simulated timber visually match the experimental tree. (C) Quantitative comparability of timber utilizing phylogenetic abstract statistics present some simulations (dots) agree with information (dashed line) and that mannequin run introduces probably the most variability (stable coloured traces are medians throughout sequence sampling and BEAST run).
To quantitatively evaluate timber, phylogenetic abstract statistics from every simulated tree and the experimental tree have been examined (Fig. 4C): common tMRCA, Sackin’s index (a tree stability statistic calculated because the sum over the variety of inner nodes between root and tip for all ideas within the tree) (49), and the dominant eigenvalue of the tree’s modified graph Laplacian spectrum (MGL). MGL is a sturdy measurement of tree form that quantifies deep/shallow branching occasions and importantly was proven to be a surrogate for synonymous to nonsynonymous (dN/dS) ratio, a metric typically used to quantify choice (50). Mannequin run 3 (greens) matched experimental statistics nicely. Though sampling and tree estimation stochasticity affected abstract statistic values, probably the most vital variability was launched by rerunning the mannequin—significantly common tMRCA (Fig. 4C; horizontal traces present median throughout sampling and tree estimation).
This course of additionally highlights the potential for misclassifications within the absence of detailed inhabitants dynamics. This train employed the best assumption of fixed inhabitants dimension in BEAST. As a result of viral masses peak early in an infection, the tree inference considerably overestimated the gap between the foundation and the founder sequence: The purple samples noticed at day 8 of an infection have been positioned within the most clade credibility tree at ∼100 d. Such artifacts is likely to be overcome with extra sophisticated inhabitants dynamic fashions in BEAST. But, current work on beginning–demise fashions with time-varying charges confirmed completely different eventualities generate the identical timber such that eventualities should not distinguishable even with infinite information (51). One other speedy problem arises from constructing bifurcating fairly than polytomic timber on information from the simulation. The current mannequin permits for a single ancestor to supply many various offspring variants with out intermediates (polytomy)—thus further inner nodes inferred by a bifurcating tree could also be artifacts—a degree warranting additional investigation.
Dialogue
By modeling human HIV information together with viral inhabitants sizes and evolutionary dynamics, we uncovered a number of vital traits of HIV pathogenesis. Probably the most parsimonious mannequin was ruled by 1) an inherited distribution of viral infectivity drawn from an exponential distribution such that 2) most mutants are much less match than parental sequences. This distribution in flip implies a virtually impartial evolutionary course of pushed by intrinsic fluctuations in viral health. The optimum mannequin additionally carried an adaptive immune system that was equally potent towards all variants, suggesting that 3) though adaptive immunity is required to manage viremia, within-host strain towards particular strains was not wanted to precisely mannequin viral evolution.
Collectively these findings paint an image of what’s adequate to explain early HIV an infection: a viral quasi-species by which a match variant can dominate or cocirculate with different dominant strains. Nonetheless, any mutant progeny of presently dominant variants are probabilistically more likely to be much less match such that new variants emerge and take over [similar to nearly neutral evolution (43)]. Such inhabitants sweeps are sufficiently modeled with none further strain from the immune system towards particular variants. The imprint of the founder virus can be long-lasting (Fig. 3), which ends up in a bimodal distribution of circulating variant sequence age (i.e., there’s creation of contaminated cells by current and ancestral strains) This discovering is likely to be related to understanding the discordance of within- and between-host evolutionary charges, however extra work is warranted.
Subsequent, utilizing sequence entropy from people not essentially sampled inside main an infection, we discovered our model-estimated distribution was related, suggesting that though we match our mannequin to main an infection, this distribution might maintain throughout different phases of an infection, and that evolution is likely to be pushed by intrinsic health in these phases too. Furthermore, it is likely to be questioned whether or not exponentially distributed health within the mannequin is successfully modeling adaptive immune choice. Thus, we confirmed that in vitro DMS information (which ensures no affect from adaptive immunity) have been additionally comparatively just like the model-estimated distribution (Fig. 2). These outcomes corroborated our speculation that a lot of HIV evolution is managed on the viral fairly than adaptive immune degree.
Though our outcomes indicate that adaptive immunity to HIV could also be broader and fewer straight influential on evolution than beforehand imagined, it stays a key part of viral management. This agrees with previous experimental work: The timing of CD8+ T cell enlargement correlated with reductions in viral masses (52) and depleting CD8+ T cells in SIV contaminated macaques led to viral enlargement (53) [we note other studies show inefficient infected cell killing by CD8+ T cells, suggesting a more nuanced interpretation (54)]. Moreover, as a result of our mannequin effector cell killing charge κ was a robust determinant of viral load setpoint (SI Appendix, Fig. S7), we hypothesize that the general HLA–antigen match (which depends upon the precise host and the precise virus) determines illness severity. This agrees with the discovering that sure host HLA genotypes are related to delayed development to AIDS (55) however that the founder sequence is correlated to pathogenesis (56).
There’s robust proof pointing to choice by adaptive immunity throughout power HIV an infection. Observations vary from mounted mutations that may be linked to detectable CD8+ T cell responses (31), a dose–response relationship (in a single particular person) between immune strain and escape charge (57), a rise over time of escape mutations in HLA-matched hosts relative to HLA-mismatched hosts (33), and the emergence of bNAbs (37). Our outcomes don’t invalidate these findings. As a substitute, within the context of the “red-queen phenomenon” (58), a relentless escape and chase, it could be that [as others have observed (33, 35)] sequential viral/host coevolution will not be significantly related for early HIV pathogenesis. A surprisingly related message arose from a deep evaluation of HIV and antibody repertoires sequenced from the identical people (40).
Our modeling has a number of limitations. The magnitude of our modeled adaptive immune response can’t be straight in comparison with current values from the varied research as a result of will not be exactly representing any particular cell sort (e.g., CD8+ T cells, anti-HIV antibodies, or pure killer cells) and sure solely captures the HIV-specific arm of the immune system. The panorama of HIV health prices has been modeled in additional element beforehand (59). Inclined cells are additionally not clearly outlined phenotypes. In ∼15% of cell infections viral progeny share genetic materials from two parental sequences that contaminated the identical cell (60, 61); we don’t explicitly simulate such genetic recombination. Whereas express modeling of recombination could possibly be added as described beforehand (13, 62), the current strategy successfully permits for some recombination signatures. For instance, since all mutational distances are small throughout early an infection, by permitting for a lot of level mutations in a single an infection occasion this could possibly be seen as a recombination. We don’t try to include compartmental anatomy, as an alternative counting on previous research that present HIV dynamics are fairly constant throughout tissues (63⇓–65). We don’t straight mannequin nonsynonymous to synonymous ratio (dN/dS), which has been used to show selective strain. Nonetheless, dN/dS could be tough to interpret for nonequilibrium eventualities (66) and dN/dS > 1, which suggests mutations that meaningfully change proteins (nonsynonymous mutations) usually tend to survive, will not be apparent within the first years of HIV an infection (32). Moreover, the MGL abstract statistic [a surrogate for dN/dS (50)] agreed between our model-derived phylogenetic timber and human timber sampled within the first yr of an infection.
In constructing simulated timber (Fig. 4), we additionally highlighted a number of challenges of tree estimation from actual information by which depth and granularity of sampling is restricted. Others have argued that constructive choice could be obscured by or conflated with demography (67), have proven misclassification of phylodynamic parameters (51, 68⇓–70), and demonstrated that nonequilibrium inhabitants dynamic “jackpot” occasions can resemble choice (71). Bearing these complexities in thoughts, we advocate for inclusion of inhabitants dynamic information at any time when potential and continuous enhancement of phylodynamic strategies reminiscent of ours to disentangle these exquisitely coupled processes in apply.
Future functions of WiPhy fashions abound from optimizing sampling depth for phylogenetic inference utilizing simulated information, estimating an infection timing, and modeling therapies. Our outcomes have vital ramifications for vaccine design and therapeutic software of bNAbs to complement the adaptive immune system. As within-host viral genetic information proceed to be collected in remedy and prevention trials, phylodynamic fashions will probably be essential for exact and complete interpretation.
Supplies and Strategies
Mathematical Description of the Mannequin.
The mannequin (Fig. 1) accommodates cells inclined to HIV an infection S, that are created with charge and die with charge . HIV an infection begins with the introduction of a founder HIV sequence with genotype g as an intact actively contaminated cell (superscript * denotes intactness). Contaminated cells produce virions and intact virions infect new cells with charge . Unproductive virions are additionally produced (therefore empty superscript parentheses) from faulty lively contaminated cells (see third equation in Eq. 1) however can’t go on to contaminate different cells.
When a brand new cell is contaminated, mutations happen with charge μ. Given mutation, the proviral sequence is undamaged with likelihood τ. A small proportion of contaminated cells enter one in every of two latent states with the small likelihood , the place subscript s additional subdivides latent lessons to fulfill noticed multiphasic decay patterns (72). Thus, we’ve three potential contaminated cell states, which might every be intact or faulty—for brevity we categorical as . The principles of the mechanistic mannequin could be roughly expressed as set of differential equations ( denotes time spinoff) that grows as genotypes are added. After every time step, new sequences are added by mutation such that .
[1]
The generic creation and removing charges of every sort of contaminated cell is ruled by the beginning and demise vectors and such that, for instance,
[2]represents the speed of creation of lively cells of 4 varieties: faulty mutated, intact mutated, faulty nonmutated, and intact nonmutated. There are copies of those beginning and demise vectors for every general contaminated cell state .
The removing charge of every sort of contaminated cells depends upon their state, intactness, and genotype , and the speed itself may also be completely different features of the variety of cells of that state. These guidelines differ in every of the adaptive immune (ai) fashions described under. Moreover, latently contaminated cells proliferate (added to the beginning vector with charge for all intactness/genotypes) and die (added to the demise vector with charge for all intactness/genotypes) and reactivate to an lively state (added to the demise vector with charge for intact genotypes).
To mannequin mutational modifications, we modify the HDs of mutated sequences by drawing a Poisson distributed variety of nucleotide modifications . For intact mutants we use a median of 1 nucleotide substitution and for defectives—sometimes generated by APOBEC hypermutation or massive insertions/deletions—we use , the place 40 is the common variety of base pair modifications for DNA (73).
Viral Health (vf) Fashions.
We created 4 fashions for the viral health (vf) of mutated intact sequences (Fig. 1C). The primary is a trivial mannequin the place every viral pressure has the identical health. Thus, , the place d is the Dirac delta operate equal to zero until . The second assumes no inheritance from parental strains such that health modifications are uniformly distributed as much as a most worth . The third and fourth fashions assume heritability of viral health, both with an exponential distribution with charge Λ or a Gaussian distribution . Nonetheless, in each instances we additionally implement the constraint that . From a organic perspective, these fashions embody a broad vary of prospects for phenotypic variation, starting from easiest (fixed), to most complex (regular and exponential) which have symmetric or uneven health (74). These selections are additionally justified by most entropy distributions (75).
Adaptive Immune (ai) Fashions.
The genotype-dependent demise charge of actively contaminated cells is used to include six fashions of the ai response. The primary mannequin has no adaptive immunity such that .
The following two fashions have “implicit immunity,” that means that there are not any further compartments to signify immune cells. Within the strain-size mannequin, . We interpret this to imply that the variety of actively contaminated cells with viral genotype g attracts immune cells relative to that genotype’s abundance. Extra ample genotypes are eliminated quicker. Price is the utmost and parameterizes maximal charge saturation. Within the strain-age mannequin contaminated cell demise depends upon genotype age, . This may be interpreted to imply older sequences have had extra time to accrue adaptive immune strain and thus are eradicated extra quickly—a mechanism which enforces pressure alternative based mostly on magnitude of charge fixed .
The remaining variations explicitly mannequin immunity. We add a state variable compartment representing effector cells ruled by
[3]
This a part of the biology is the least understood and our mechanistic implementations might successfully seize a number of forms of cells or molecules (CD8+ T cells, NK cells, and antibodies). We draw inspiration for building from our prior work and printed fashions of immune methods in viral dynamics (76⇓⇓–79).
In strainwise immune fashions, effector cells have their very own genotype g which matches a viral genotype. Then, immune cells develop based mostly on the prevalence of their cognate antigenic genotype (time period with nonlinear development charge ω and saturation fixed ), die naturally with charge , and have one other demise time period such that the entire adaptive immune response (sum over genotypes) is constrained in dimension (time period with saturation fixed ). Within the world mannequin, . We interpret this to indicate that there’s a single adaptive immune compartment that may kill any pressure. Within the strain-specific mannequin, . We interpret this to indicate that for every viral pressure there’s an adaptive immune compartment that may kill solely that pressure. The killing capability of every strain-specific adaptive immune compartment is . Within the strain-group mannequin, . We interpret this to imply there’s some cross-immunity such that sequences with related sequence numbers (inside a bunch the place every group has the identical dimension G) could be killed by a single immune compartment with killing charge which is assumed the identical for all teams. The demise charge of latently contaminated cells is easier, and charges should not depending on values, as an alternative such that intact cells die barely quicker in accordance with noticed values.
Parameters from the Literature.
By utilizing earlier estimates, we constrained the parameters that have to be estimated. All info on mounted parameters, preliminary circumstances, and match parameter ranges is contained in SI Appendix, Table S3. Three parameters are estimated in all fashions, and completely different fashions have additional parameters that have to be estimated such that outcomes vary from three to 9 estimated parameters.
Simulation Implementation.
The mannequin is applied in C++ and is freely obtainable (https://github.com/FredHutch/WiPhy_HIV). We use a discrete stochastic τ-leap simulation scheme in 10 mL of plasma and a simulation time interval of Δt = 0.01 d. The state variables signify the numbers of inclined, lively/latent contaminated cells and virions (for every genotype) and adaptive immunity if explicitly within the mannequin. Thus, in every time interval, a Poisson-distributed variety of occasions of every mechanistic transition is chosen by the response propensities (80) such that . Then, the state variables are up to date utilizing the occasion transition matrix T as . For instance, in an interval we’d observe the creation of a brand new latently contaminated cell of a brand new genotype by viral an infection. For this instance, , that means removing of a inclined cell, removing of an intact virion of genotype g, and the creation of an intact first section latently contaminated cell with genotype . On this similar interval many different occasions might happen concurrently.
Monitoring the Full Transmission File (Family tree).
To seize evolution, every viral pressure is given a genotype quantity (an integer g). This quantity specifies an health/infectivity (), the variety of base-pair mutations for this genotype relative to the founder virus (the HD ), its age ( the date of its emergence in time for the reason that begin of an infection), and the variety of every nucleic acids ( the place and the preliminary quantity is taken from the reference HXB2 sequence). The variety of every state variable (e.g., contaminated cells) related to that genotype is recorded at every time step. A considerable computational enhancement was achieved by monitoring inhabitants dimension however not attributes and transmission information for faulty variants. This alternative is effective as a result of hypermutants and/or massive deletions are sometimes eliminated earlier than evaluation of experimental information, however modeling the variety of faulty sequences was essential to precisely populate the latent reservoir, which is well-known to be predominantly faulty (81).
Mannequin Becoming Process.
The perfect parameterization of every mannequin was achieved by testing 100 values of every parameter, the place the variety of mannequin parameters is okay. This strategy implies that for a mannequin with eight parameters, a complete of 800 × 8 = 6,400 parameterizations have been examined, i.e., extra advanced fashions had extra alternatives to seek out an optimum. Values have been drawn from a grid search evenly spaced between a decrease and higher sure for every parameter (typically a number of orders of magnitude) based mostly on beforehand decided HIV mannequin charges. As a result of the mannequin is stochastic, we tried 20 replicate simulations for every parameter set, stopping if 10 replicates have been profitable. Every replicate was scored by computing the mannequin worth of every metric () and computing a variance-normalized residual sum of squares (, additionally known as the statistic) towards the metric from the info: , the place is the experimentally decide metric; the overbar denotes the imply and var denotes the variance or squared SD. We additionally calculated the entire RSS because the sum .
Mannequin Choice.
As a result of we match to correlated metrics and mixed information sources, we dominated out typical mannequin choice procedures based mostly on likelihoods and data standards (e.g., Akaike info criterion). As a substitute, we utilized an ABC strategy. The normalized RSS was calculated for every metric and runs with all particular person metrics becoming fairly nicely () have been included. SI Appendix, Fig. S1 reveals the RSS summed over particular person metrics. We decided the most effective single run for the most effective parameter set, for every mannequin. Then, to choose fashions that persistently work nicely, we finally accepted mannequin parameterizations for which mannequin output averaged throughout stochastic runs was inside our RSS tolerance.
World Sensitivity Evaluation.
Utilizing the most effective mannequin, we quantified the affect of mannequin parameters on all metrics, and on the RSS error of all metrics, utilizing world sensitivity evaluation by calculating the Spearman correlation coefficient (SI Appendix, Fig. S7) (82).
Modeling Comparability to Entropy Distributions.
We obtained filtered HIV-1 env alignments (sort M with out recombinants) from the LANL database (https://www.hiv.lanl.gov/content/index) and eliminated all however subtype B sequences leading to 2,339 sequences. Entropy was calculated with default choices on the LANL web site and gaps are eliminated to resolve the consensus sequence and its entropy values. The relative abundance of every base b at every place ψ within the env is expressed such {that a} completely even distribution at some place is written , whereas a wonderfully uneven distribution at some place is written , which represents {that a} single base (e.g., T) is discovered at that place for all people within the database. We calculated Shannon’s entropy for every place. Subsequent, as a result of our mannequin is agnostic to nucleotide-position-specific biology, we reranked entropy from most to least variable. We then use the distribution of entropy as a quantitative estimate of the relative impact of lowering health after a degree mutation to positions in env. We then recognized the issue y that may scale entropy (assumed fixed over place) such that most intently resembled our best-fit viral-fitness distribution . We minimized the RSS between information and mannequin distributions to seek out 1.5.
Sequence Sampling.
To simulate sampling, we randomly choose virions (recapitulating experimental sampling of viral RNA) from the simulation. On the time intervals matching the experimental information, cells are computationally sampled from the current virus till a given variety of sequences are represented or till all lively sequences are represented if the precise quantity is much less.
Calculating tMRCA.
Time to most up-to-date widespread ancestor (Fig. 3) was calculated by inspecting all sequence pairs and figuring out their parental sequence. If the father or mother is similar, the process halts and the beginning date of the father or mother is recorded as tMRCA. If the father or mother is completely different, we observe again to folks of the parental sequences and repeat.
Calculation of Divergence and Variety.
As a result of we don’t observe nucleotide sequences, to calculate the variety of base-pair variations between a pair of sequences we compute the sum of their HDs and subtract off the HD of their parental sequence . The divergence is calculated because the the place is the founder sequence. Variety is calculated as the common pairwise distance (83):
[4]the place the frequency of every sampled variant is , the place N is the entire pattern dimension and the variety of nucleotides l is the size of HIV env.
Integration with BEAST.
To harmonize simulation output with phylogenetic inference instruments, we used genealogies and HDs to output an inventory of sampled nucleotide sequences. We utilized an HKY nucleotide substitution mannequin starting with the HXB2 reference and protecting a hard and fast size genome to export a time labeled FASTA file which could be enter to BEAST. Notice that this coarse put up facto web site mannequin could possibly be expanded to incorporate insertions and deletions however not recombination presently. Our mannequin allowed for HKY variable frequency of transitions and transversions such that ahead simulation and backward inference was congruent. We selected a strict molecular clock and a hard and fast inhabitants dimension and ensured convergence by testing completely different burn-in sizes. An instance XML file by which BEAST settings could be discovered is supplied inside our GitHub repository.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by a Washington Analysis Basis postdoctoral fellowship and a Nationwide Institute of Allergy and Infectious Illnesses K25 (AI155224) to D.B.R. D.B.R. is grateful to quite a few colleagues for conversations together with F. Boshier, A. Dingens, T. Bedford, B. Dearlove, E. Lewitus, A. Feder, P. Roychoudury, P. Edlefsen, and J. Mullins.
Footnotes
- Accepted December 16, 2021.
-
Creator contributions: J.T.S. and D.B.R. designed analysis; D.A.S. and D.B.R. carried out analysis; M.R. and D.B.R. contributed new reagents/analytic instruments; D.A.S. and D.B.R. analyzed information; and D.A.S., M.R., J.T.H., J.T.S., and D.B.R. wrote the paper.
-
The authors declare no competing curiosity.
-
This text is a PNAS Direct Submission.
-
This text accommodates supporting info on-line at https://www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.2109172119/-/DCSupplemental.
- Copyright © 2022 the Creator(s). Printed by PNAS.
Comments
0 comments