Significance
Evolutionary branching and diversification in interactions with steady behavioral traits is vital for understanding the emergence of distinct, discrete, and coexisting methods. In social dilemmas, this means an evolutionary pathway for the origin of cooperators and defectors. Right here we examine evolutionary diversification in structured populations and determine mechanisms driving spontaneous and chronic diversification. By analytical and numerical methods, we reveal that spatial construction admits new modes of diversification that complement classical evolutionary branching. Specifically, when choice is robust, diversification tends to happen extra readily than in unstructured populations.
Summary
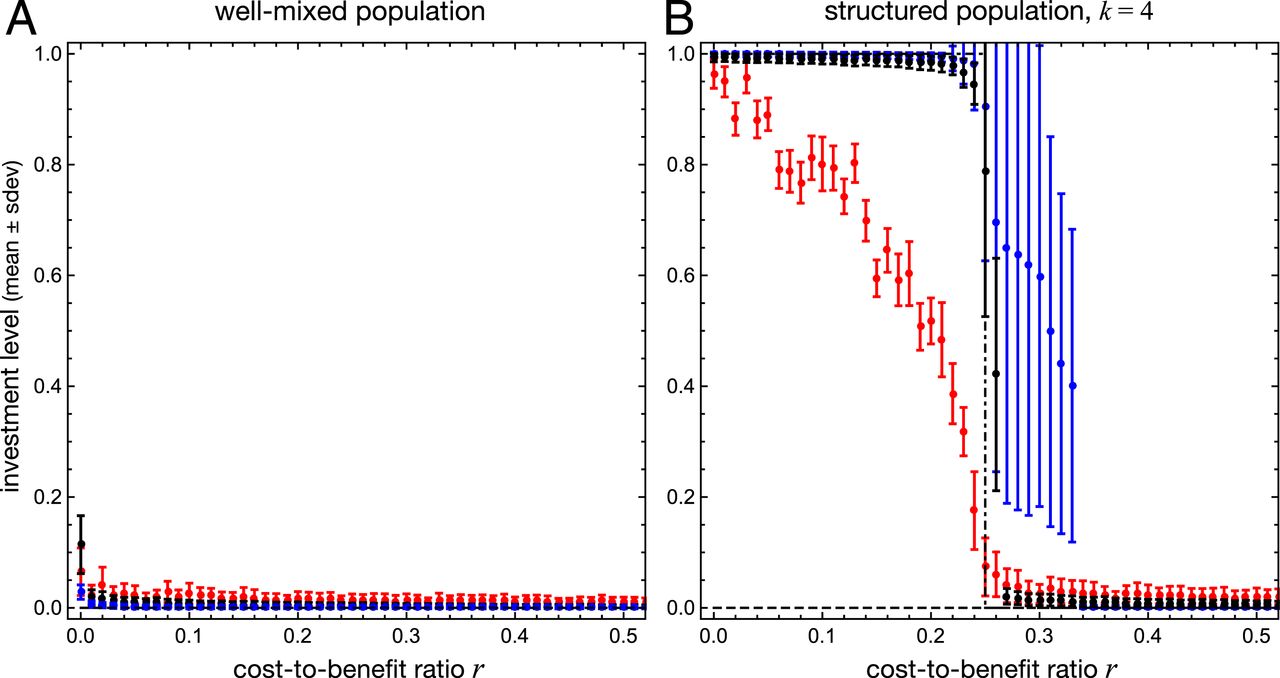
Cooperative investments in social dilemmas can spontaneously diversify into stably coexisting excessive and low contributors in well-mixed populations. Right here we lengthen the evaluation to rising variety in (spatially) structured populations. Utilizing pair approximation, we derive analytical expressions for the invasion health of uncommon mutants in structured populations, which then yields a spatial adaptive dynamics framework. This enables us to foretell adjustments arising from inhabitants constructions when it comes to existence and site of singular methods, in addition to their convergence and evolutionary stability as in comparison with well-mixed populations. Primarily based on spatial adaptive dynamics and intensive individual-based simulations, we discover that spatial construction has vital and diverse impacts on evolutionary diversification in steady social dilemmas. Extra particularly, spatial adaptive dynamics means that spontaneous diversification by evolutionary branching is suppressed, however simulations present that spatial dimensions provide new modes of diversification which can be pushed by an interaction of finite-size mutations and inhabitants constructions. Despite the fact that spatial adaptive dynamics is unable to seize these new modes, they will nonetheless be understood primarily based on an invasion evaluation. Specifically, inhabitants constructions alter invasion health and may open up new areas in trait house the place mutants can invade, however that is probably not accessible to small mutational steps. As an alternative, stochastically showing bigger mutations or sequences of smaller mutations in a selected course are required to bridge areas of unfavorable traits. The web impact is that spatial construction tends to advertise diversification, particularly when choice is robust.
Comments
0 comments